Introduction
Graph databases have gained immense popularity in recent years due to their efficiency in handling complex and interconnected data. Among these, Neo4j stands out as one of the most widely used and robust graph databases. Unlike traditional relational databases, which rely on tables and rows, Neo4j leverages a graph model that consists of nodes, relationships, and properties. This structure allows for efficient querying and data traversal, making it ideal for use cases such as social networks, fraud detection, recommendation systems, and knowledge graphs.
In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of graph databases, delve into the core features of Neo4j, understand indexing in Neo4j, and discuss best practices for optimizing performance.
1. Fundamentals of Graph Databases
1.1 What is a Graph Database?
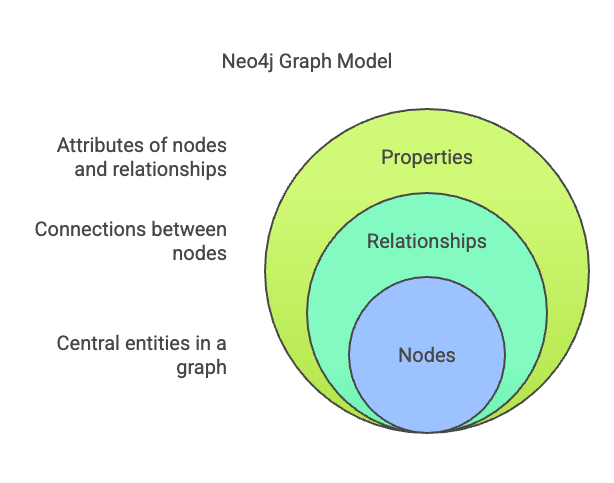
A graph database is a type of NoSQL database designed to store and manage data using graph structures. It consists of:
- Nodes: Represent entities such as people, organizations, or products.
- Relationships: Represent the connections between nodes, such as friendships or purchases.
- Properties: Attributes that describe nodes and relationships.
1.2 Graph Data Model
Unlike relational databases that rely on JOIN operations to connect data, graph databases store relationships natively, allowing for highly efficient traversal operations. This structure significantly improves query performance for connected data.
1.3 Advantages of Graph Databases
- Performance: Fast data retrieval through relationships.
- Flexibility: Schema-less model for easy data evolution.
- Intuitive Modeling: Matches real-world scenarios naturally.
- Efficient Traversal: Eliminates costly JOIN operations.
2. Introduction to Neo4j
2.1 What is Neo4j?
Neo4j is a native graph database that enables efficient graph processing and analytics. It supports ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties, ensuring data integrity and reliability.
2.2 Neo4j Data Model
Neo4j follows a property graph model consisting of:
- Nodes – Entities with labels and properties.
- Relationships – Directed and labeled connections between nodes.
- Properties – Key-value pairs attached to nodes and relationships.
2.3 Cypher Query Language
Neo4j uses Cypher, a declarative query language optimized for graph traversal. Some common Cypher commands include:
// Create a node
CREATE (p:Person {name: 'Alice', age: 30})
// Create a relationship
MATCH (a:Person {name: 'Alice'}), (b:Person {name: 'Bob'})
CREATE (a)-[:FRIEND]->(b)
// Query data
MATCH (p:Person) RETURN p.name, p.age
3. Indexing in Neo4j
3.1 What is an Index?
An index is a data structure that improves search performance by allowing faster lookups. In Neo4j, indexing helps locate nodes and relationships efficiently.
3.2 Types of Indexes in Neo4j
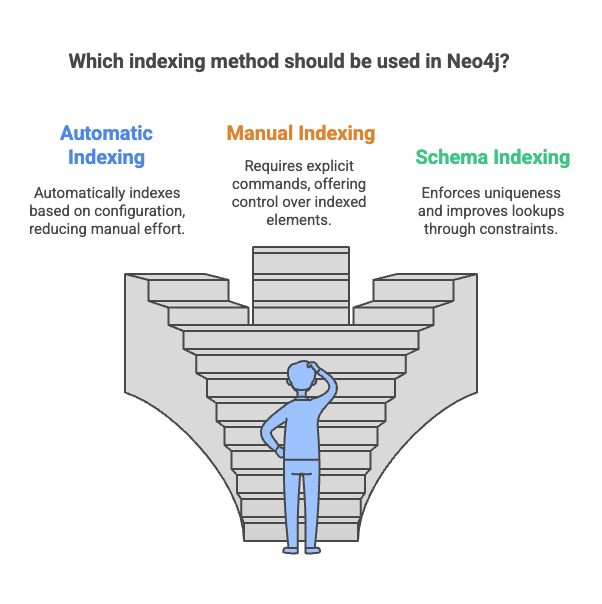
- Automatic Indexing:
- Automatically indexes node and relationship properties based on configuration.
- Manual Indexing:
- Requires explicit commands to add or remove indexed elements.
- Schema Indexing:
- Uses constraints to create indexes on properties to enforce uniqueness and improve lookups.
3.3 Creating and Using Indexes
3.3.1 Creating an Index
You can create an index using Cypher:
CREATE INDEX FOR (p:Person) ON (p.name)
This index speeds up queries that filter by name.
3.3.2 Unique Constraints
To enforce uniqueness:
CREATE CONSTRAINT FOR (p:Person) REQUIRE p.email IS UNIQUE
This ensures that no two nodes have the same email property.
3.3.3 Listing Indexes
To check existing indexes:
SHOW INDEXES
3.3.4 Dropping an Index
DROP INDEX index_name
3.4 When to Use Indexes
- When performing lookup queries based on specific properties.
- When enforcing uniqueness constraints.
- When optimizing queries that frequently search based on node labels and properties.
3.5 When Not to Use Indexes
- When data retrieval relies on graph traversal instead of direct lookup.
- When dealing with small datasets where indexing overhead outweighs benefits.
- When relationships are frequently updated as index maintenance can slow down performance.
4. Optimizing Performance in Neo4j
4.1 Query Optimization with Indexes
- Use indexed properties in WHERE clauses:
MATCH (p:Person) WHERE p.name = 'Alice' RETURN p
- Avoid full graph scans by using indexes where applicable.
- Use constraints to enforce data integrity and enhance query performance.
4.2 Profiling and Debugging Queries
Neo4j provides tools to analyze query performance:
- EXPLAIN: Shows execution plan without running the query.
EXPLAIN MATCH (p:Person) WHERE p.name = 'Alice' RETURN p
- PROFILE: Runs the query and provides execution details.
PROFILE MATCH (p:Person) WHERE p.name = 'Alice' RETURN p
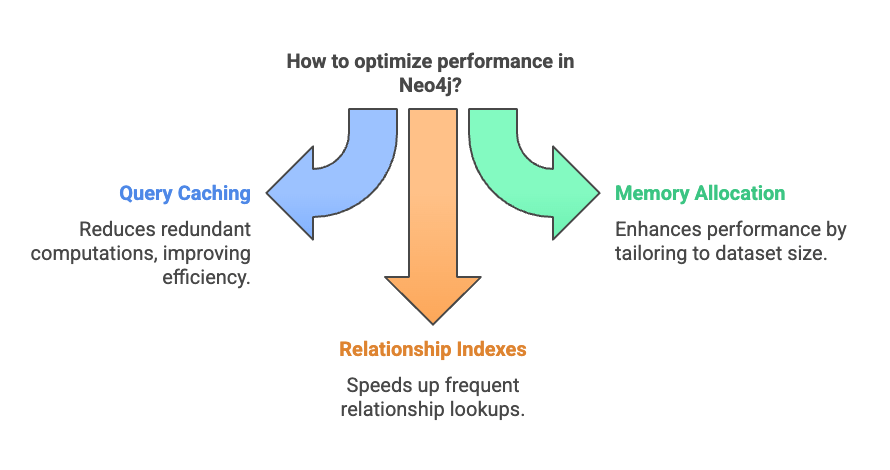
4.3 Caching Strategies
- Use query caching to avoid redundant computations.
- Optimize memory allocation based on dataset size.
- Use relationship indexes for frequent relationship lookups.
5. Use Cases of Neo4j
5.1 Social Networks
- Friend recommendations based on mutual connections.
- Community detection using graph algorithms.
5.2 Fraud Detection
- Anomaly detection by analyzing transaction relationships.
- Pattern recognition for identifying fraudulent activity.
5.3 Recommendation Systems
- Product recommendations based on user interactions.
- Graph-based ranking algorithms like PageRank.
5.4 Knowledge Graphs
- Semantic search by linking related concepts.
- Data integration from diverse sources into a connected graph.
Neo4j offers a powerful and flexible approach to handling connected data efficiently. With its native graph storage, Cypher query language, and advanced indexing capabilities, Neo4j is well-suited for applications that require fast traversal and deep relationship analysis. By leveraging indexing, constraints, and performance optimizations, organizations can unlock the full potential of graph databases for real-world use cases like social networks, fraud detection, and recommendation systems.
Understanding and implementing indexing in Neo4j is critical for improving query performance and ensuring scalable database operations. By following best practices for index usage, developers can build high-performance applications that fully harness the power of graph databases.
Leave a comment