
Introduction to Spring
Spring is an open-source application framework for Java, designed to simplify enterprise software development. It provides a comprehensive infrastructure for building web applications, enterprise software, and microservices. The Spring ecosystem offers a robust set of tools, frameworks, and libraries that streamline the development process.
What is Spring Framework?
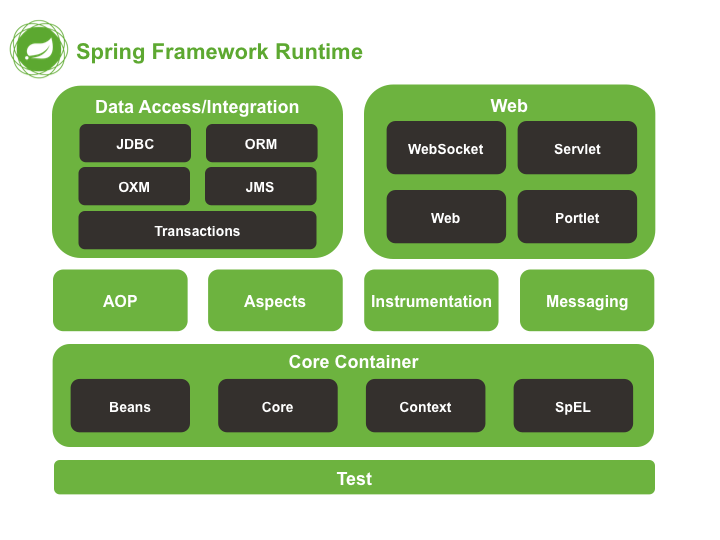
Spring Framework, also known as Spring, is a Java application framework that enables developers to build enterprise-level applications. It provides a modular, lightweight, and flexible architecture for building complex systems. The framework’s primary goal is to simplify Java development by:
- Providing a consistent and modular framework
- Enabling dependency injection
- Supporting aspect-oriented programming (AOP)
- Facilitating transaction management
- Integrating with various databases and technologies
Key Features of Spring Framework:
- Dependency Injection: Spring’s IoC (Inversion of Control) container manages dependencies between objects.
- Aspect-Oriented Programming: Spring supports AOP for modularizing cross-cutting concerns.
- MVC Framework: Spring provides a robust MVC framework for web applications.
- Transaction Management: Spring simplifies transaction management for database interactions.
- Security: Spring Security provides robust security features for authentication and authorization.
What is Spring Boot?
Spring Boot is a microframework built on top of the Spring Framework. It provides a streamlined approach to building production-grade Spring applications with minimal configuration. Spring Boot aims to:
- Simplify Spring application development
- Provide auto-configuration for common tasks
- Offer production-ready features (e.g., metrics, health checks)
- Enable fast deployment and development
Key Features of Spring Boot:
- Auto-Configuration: Spring Boot automatically configures dependencies.
- Starter Dependencies: Simplified dependency management using starter dependencies.
- Embedded Servers: Spring Boot includes embedded servers (Tomcat, Jetty).
- Metrics and Monitoring: Built-in support for metrics and monitoring.
- Quick Startup: Fast application startup.
Components of Spring Framework:
- Spring Core: Provides the fundamental framework for dependency injection.
- Spring MVC: A web framework for building web applications.
- Spring Data: Simplifies database interactions (e.g., JDBC, Hibernate).
- Spring Security: Provides authentication, authorization, and security features.
- Spring Integration: Enables integration with external systems and messaging.
- Spring Batch: Supports batch processing and job scheduling.
- Spring Cloud: Provides cloud-native features for distributed systems.
Components of Spring Boot:
- Spring Boot Starters: Simplified dependency management.
- Auto-Configuration: Automatic configuration for dependencies.
- Embedded Servers: Tomcat, Jetty, and Undertow.
- Spring Boot Actuator: Production-ready features (metrics, health checks).
- Spring Boot DevTools: Development tools (e.g., auto-restart).
Use Cases:
- Web Development: Spring MVC and Spring Boot for web applications.
- Microservices: Spring Boot and Spring Cloud for distributed systems.
- Enterprise Software: Spring Framework for complex, scalable systems.
- Big Data: Spring Data and Spring Batch for data processing.
Spring, Spring Framework, and Spring Boot provide a robust ecosystem for building enterprise-level applications. Understanding the components and features of each enables developers to choose the best tool for their specific needs.